다른 나라는 2.5%, 0%와 같이 특정 값인데 왜 미국은 3.0%~3.25%와 같이 구간으로 표시할까.
더군다나 구간의 아래 수치는 의미가 없는거 같은데 사이트를 찾아봐도 잘 모르겠네.
이건 그냥 이 수준에서 이해하고 넘어가는게 좋겠다.
확인한 사항
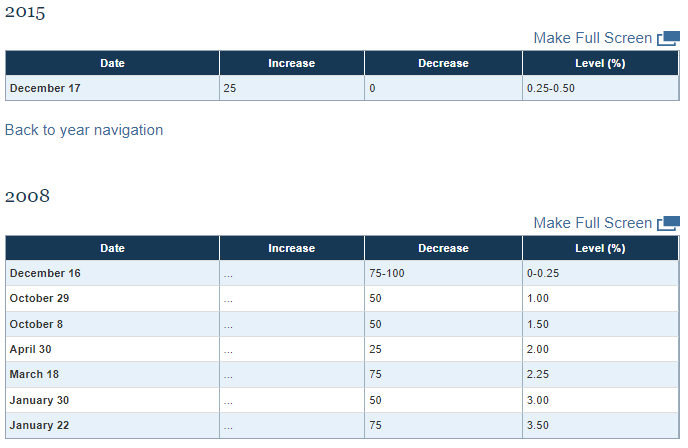
- 미국도 2008년 12월 이전에는 1.5%, 1.0%과 같이 하나의 값으로 설정 → 2008년 12월에 0.0~0.25%구간으로 설정
- 2008년 12월부터 구간으로 바뀐건데, 왜 그런건지를 모르겠네
- FED 설명에는 금융위기때인 2008년 말 Near-zero로 했다는데 왜 딱 0%로 안하고 구간으로 한건지는 잘 모르겠네
- 중앙일보에도 뭔가 설명이 있는데 내가 이해력이 부족해서 그런지 '왜' 그렇게 했다는건지 잘 모르겠음
금융위기때 말은 0.25%로 했지만 거의 0%나 다름없다는 건데, 그냥 0%로 하면 뭔가 충격을 받을까봐 그런건가..?
< FED 설명 >
Open Market OperationsOpen market operations (OMOs)--the purchase and sale of securities in the open market by a central bank--are a key tool used by the Federal Reserve in the implementation of monetary policy. The short-term objective for open market operations is specified by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). Before the global financial crisis, the Federal Reserve used OMOs to adjust the supply of reserve balances so as to keep the federal funds rate--the interest rate at which depository institutions lend reserve balances to other depository institutions overnight--around the target established by the FOMC.The Federal Reserve's approach to the implementation of monetary policy has evolved considerably since the financial crisis, and particularly so since late 2008 when the FOMC established a near-zero target range for the federal funds rate. From the end of 2008 through October 2014, the Federal Reserve greatly expanded its holding of longer-term securities through open market purchases with the goal of putting downward pressure on longer-term interest rates and thus supporting economic activity and job creation by making financial conditions more accommodative. During the policy normalization process that commenced in December 2015, the Federal Reserve first used overnight reverse repurchase agreements (ON RRPs)--a type of OMO--as a supplementary policy tool, as necessary, to help control the federal funds rate and keep it in the target range set by the FOMC. *https://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/openmarket.htm |
< 중앙일보 기사 >
| Fed가 발표하는 연방기금금리는 단기시장 금리를 그 수준에 맞추겠다는 목표금리 성격이다. 금리는 시장에서 수요와 공급에 따라 결정되지만 기준금리 범위를 넘어섰을 때 중앙은행이 개입해 조정한다. 금융위기 때 페니메와 프레디맥이 부실화되자 미국 정부는 공적 자금을 투입해 두 회사를 살렸다. 이후 미 정부는 두 회사가 이익을 내면 다른 자산 등에 투자하지 못하게 하고 단기 금융시장에 이익금을 공급하는 걸 의무화했다. 두 회사가 이익금을 금융시장에 공급하자 단기금리가 떨어져 연방기금금리 목표치에서 멀어졌다. 예컨대 연방기금금리가 0.25%였지만 실제 시장 금리는 0.13~0.14%에서 움직였다. 시장에서 목표치와 실제 금리의 격차가 커지자 Fed는 2008년 12월 말부터 연방기금금리를 0~0.25% 구간으로 정했다. 시장 금리를 연방기금금리 범위 안에 두기 위해서다. *https://www.joongang.co.kr/article/19268534#home |
< 기준 금리 >
'소소하게 알아가는 즐거움 > 미국 경제지표' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 케이스-쉴러 주택가격지수가 CPI 주거비 항목의 선행지수? (8) | 2022.10.20 |
|---|---|
| 미국 CPI 항목별 트렌드 (10) | 2022.10.20 |
| 미국 CPI, PCE 가격지수 산출방식 차이 (6) | 2022.10.13 |
| UN, IMF, FED.. 그래서 금리는 어디로? (14) | 2022.10.08 |
| 미국 GDP, PCE, PCE 물가지수 (2) | 2022.10.01 |



